
Nightingale has analysed more than 1 million blood samples from more than 20 different countries.
My Nightingale's proprietary algorithms are based on large representative population datasets including blood test results and disease history.
In addition, the algorithms have been further validated for Japanese population using blood samples from Japanese individuals.
Quantitative analysis of blood biomarkers from a large sample collection from a Finnish biobank
Blood samples of tens of
thousands of individuals
Quantitative analysis of
blood biomarkers

Health profiles of
20 000 people

Reviewing the disease history during 10 years after blood sample collection
Identification of individuals who
developed lifestyle-related diseases
In order to create disease risk prediction algorithms, artificial intelligence is used to find unique biomarker signatures in disease-prone individuals.
In collaboration with a biobank in Japan, we have further validated the algorithm for Japanese population using blood samples from Japanese individuals.
Biomarker signatures of disease onset
Algorithms for disease risk prediction

Nightingale uses innovative measurement technology based on NMR (Nuclear Magnetic Resonance) to quantitatively analyze 250 blood biomarkers from each blood sample. The analysis is also widely used for research purposes and there are more than 300 scientific publications utilizing the Nightingale technology.
The technology is highly evaluated by scientific institutions and biobanks around the world, demonstrated by several collaborative initiatives. More than one million blood samples have been analyzed by Nightingale. Among others, Nightingale is currently measuring all 500 000 blood samples from the UK Biobank.

Blood samples

NMR

250 biomarkers from
each blood sample

AI and machine
learning algorithms
Automated
laboratory
processes
Advanced
software

High-speed processing

High accuracy

Consistent results

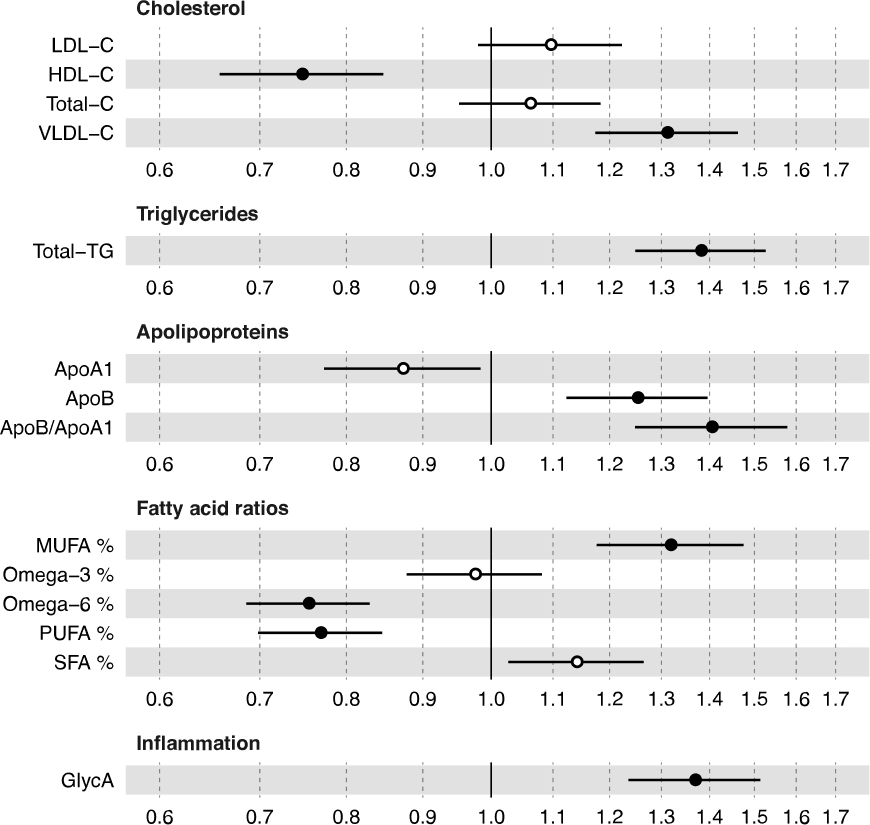
OR for incident type 2 diabetes (95% CI),
per 1−SD increment in log−transformed biomarker concentration (ORs were adjusted for sex, baseline age, BMI and fasting glucose)
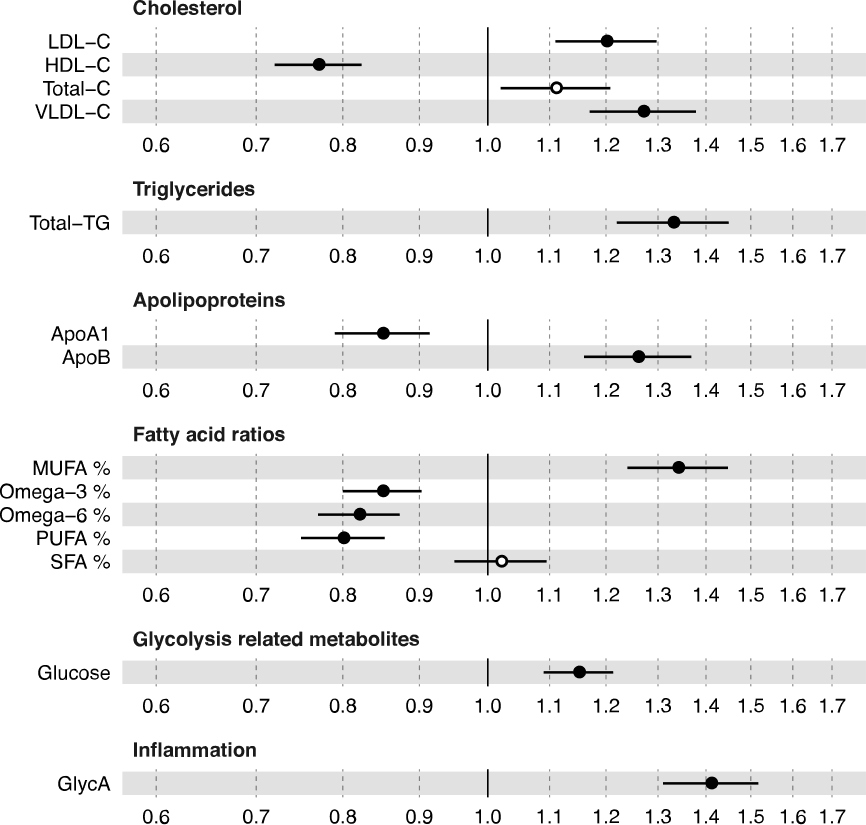
HR for incident cardiovascular disease (95% CI),
per 1−SD increment in log−transformed biomarker concentration (HRs were adjusted for sex and baseline age)